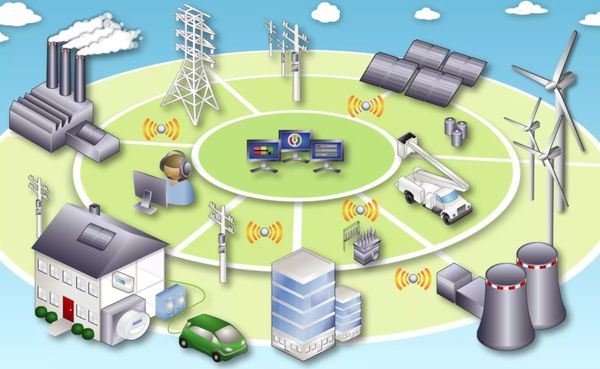
The term Smart Grid is most commonly defined as an electrical grid that has been digitized to provide two-way communication between producers and consumers. The goal of the Smart Grid is to upgrade the electric power infrastructure to include more advanced communication, control and sensor technologies, with the hope of increasing interaction between consumers and power producers. Potential benefits of the Smart Grid include increased reliability, more efficient use of electricity, better economics and increased resilience. The Smart Grid concept began to emerge in the early 2000s. Since then, many countries have been striving for smart grids. Smart grids of local character are clusters that in case of failure of the common external system are able to work autonomously. Their creation entails improvement and replacement of power transforming equipment, switchgears, transmission lines, automated control systems, metering, communications.
Smart grid support became federal policy with the passage of the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 . The law,provides $100 million in funding for fiscal years 2008 through 2012, establishes a matching program for states, utilities, and consumers to build smart grid capabilities, and creates a Grid Modernization Commission to evaluate the benefits of demand response and recommend necessary protocol standards. The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 directs the National Institute of Standards and Technology to coordinate the development of smart grid standards, which FERC will then promulgate through formal rules . Smart grids received additional support with the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, which allocated $11 billion for smart grid development.
A set of technical means that automatically detect the weakest or emergency zones, as well as have the ability of self-diagnosis, are smart grids.
In order to increase the efficiency of electricity distribution, such a network consists of installations:
Smart grids do not require constant human intervention because they are systems consisting of converters of solar, water or wind energy into a resource for domestic and industrial consumption.
If we take the example of the United States, which has introduced a strategy of smart grids in economic development, we can conclude that the use of mini generators, electric cars, solar collectors allows to achieve a balance between the many producers and consumers of electricity.
Power supply systems, created by linking generators and loads in a separate service area and controlled by energy flows, are combined into the main smart grids.
Considering the assessment of experts from the United States Department of Energy, Smart Grid complexes have the following advantages:

Smart grid support became federal policy with the passage of the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 . The law,provides $100 million in funding for fiscal years 2008 through 2012, establishes a matching program for states, utilities, and consumers to build smart grid capabilities, and creates a Grid Modernization Commission to evaluate the benefits of demand response and recommend necessary protocol standards. The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 directs the National Institute of Standards and Technology to coordinate the development of smart grid standards, which FERC will then promulgate through formal rules . Smart grids received additional support with the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, which allocated $11 billion for smart grid development.
A set of technical means that automatically detect the weakest or emergency zones, as well as have the ability of self-diagnosis, are smart grids.
In order to increase the efficiency of electricity distribution, such a network consists of installations:
- communication;
- controlling;
- distribution.
Smart grids do not require constant human intervention because they are systems consisting of converters of solar, water or wind energy into a resource for domestic and industrial consumption.
If we take the example of the United States, which has introduced a strategy of smart grids in economic development, we can conclude that the use of mini generators, electric cars, solar collectors allows to achieve a balance between the many producers and consumers of electricity.
The Advantages of Smart Grids
Power supply systems, created by linking generators and loads in a separate service area and controlled by energy flows, are combined into the main smart grids.
Considering the assessment of experts from the United States Department of Energy, Smart Grid complexes have the following advantages:
- Active participation in the consumer grid;
- self-recovery in the result of power supply failures;
- high quality of incoming electric power;
- resistance to cybercrime;
- release of innovative electrical products to the international market;
- ensure synchronous operation of generation keys and power savin g nodes;
- improve overall efficiency and effectiveness of power systems.
Comments
Post a Comment